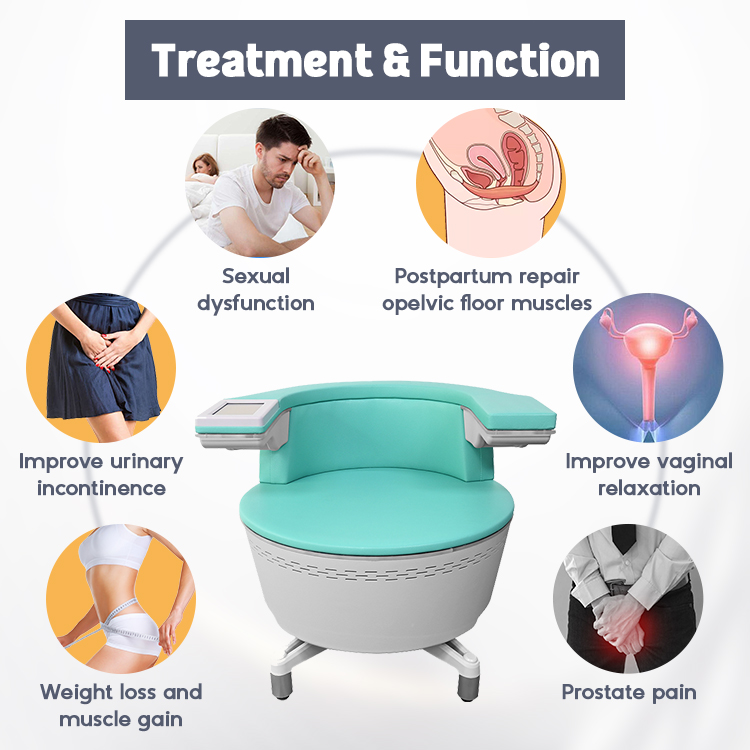
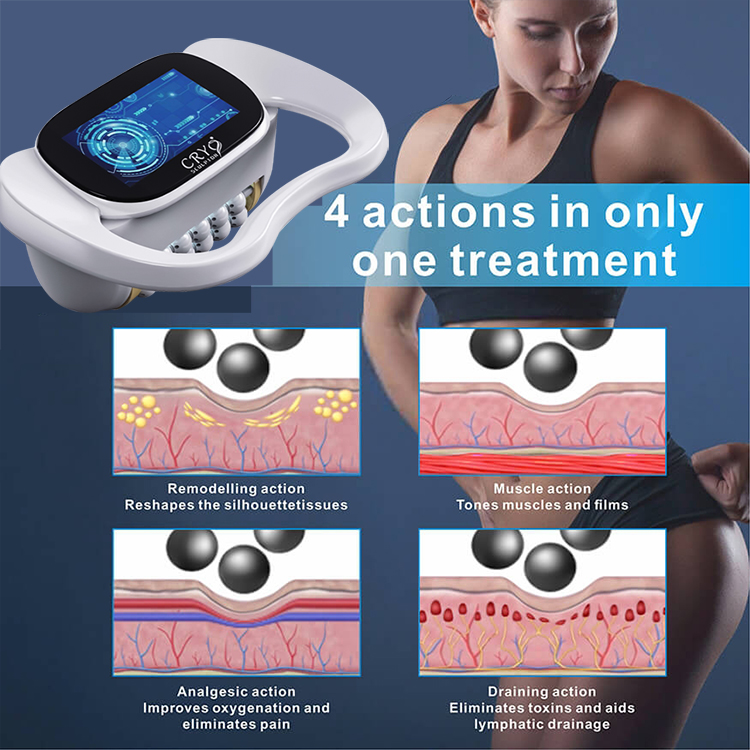
Share optimized solutions, professional valve knowledge and industry news
Please enter the relevant terms or keywords you need to consult, and relevant articles will appear in the search results. If you can’t find the answer you need, please feel free to contact us and we will be happy to help. Or you can directly send an email to beauty@shefmon.com
Which Is Stronger, TENS or EMS? A Complete Breakdown
- admin
Which Is Stronger, TENS or EMS?
When it comes to pain relief and muscle therapy, two popular devices often come up — TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) and EMS (Electrical Muscle Stimulation). They may look similar, but they work very differently. So, which one is stronger? Let’s break it down.
Understanding TENS
What Is TENS?
TENS is a therapy device that sends electrical impulses to the nerves under your skin to reduce pain. Think of it like turning off “pain signals” before they reach your brain.
How TENS Works
TENS focuses on nerve stimulation, not muscles.
It blocks pain pathways and triggers the release of endorphins — your body’s natural painkillers.
Main Uses of TENS
Chronic pain
Acute injuries
Joint and nerve pain
Back and neck pain
Post-surgery pain
Who Benefits from TENS?
Individuals with arthritis
People recovering from injury
Those with nerve-related pain or sciatica
Athletes dealing with soreness
Understanding EMS
What Is EMS?
EMS sends electrical pulses directly to muscles, causing them to contract — just like during a workout.
How EMS Works
EMS stimulates muscle fibers, improving:
Muscle strength
Recovery
Circulation
Main Uses of EMS
Strength training support
Muscle rehabilitation
Improving mobility
Reducing muscle stiffness
Who Benefits from EMS?
Athletes
Physical therapy patients
People recovering from muscle injuries
Key Differences Between TENS and EMS
| Feature | TENS | EMS |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Nerves | Muscles |
| Purpose | Pain relief | Muscle strengthening/rehab |
| Sensation | Tingling, buzzing | Muscle contractions |
| Best For | Pain management | Muscle growth & recovery |
So, Which Is Stronger — TENS or EMS?
Strength Comparison
If we’re talking powerful muscle contraction, EMS wins — hands down.
EMS produces deeper muscle stimulation, making it physically stronger.
Which Feels More Intense?
EMS also typically feels stronger since it contracts muscles.
TENS is gentler — more like tingling or buzzing.
Safety Considerations
Both are safe when used correctly, but EMS needs more caution due to its stronger action on muscles.
When Should You Choose TENS?
Best Scenarios for TENS
Use TENS if your goal is pain relief without muscle movement.
Conditions TENS Helps With
Chronic pain
Nerve pain
Arthritis
Post-surgery pain
Back and neck pain
When Should You Choose EMS?
Best Scenarios for EMS
Use EMS if your goal is muscle function and recovery.
Muscle Goals EMS Targets
Strengthening
Toning
Recovery after injury
Muscle activation before workout
Can You Use TENS and EMS Together?
Absolutely — many devices now combine both.
Example routine:
Use EMS first for activation
Use TENS after for pain relief and relaxation
This combo works great for athletes and rehab users.
Safety Tips and Precautions
Never place pads on the heart, throat, or broken skin
Consult a doctor if pregnant or using a pacemaker
Start with low intensity
Follow your device’s instructions
Conclusion
So, which is stronger — TENS or EMS?
EMS is physically stronger because it contracts muscles, while TENS is better for pain relief without muscle movement.
Both serve unique and powerful roles.
Choose based on your goal: Pain relief? Go TENS. Muscle strength or rehab? Go EMS.
FAQs
1. Can TENS build muscle?
No — TENS targets nerves, not muscles.
2. Does EMS help with pain?
Yes, but it’s mainly for muscle stimulation — not nerve pain relief.
3. Can beginners use EMS?
Absolutely — start low and increase gradually.
4. How long should I use TENS or EMS?
Usually 15–30 minutes, depending on your treatment plan.
5. Which is better for recovery after workout?
EMS — it boosts muscle recovery and blood flow.