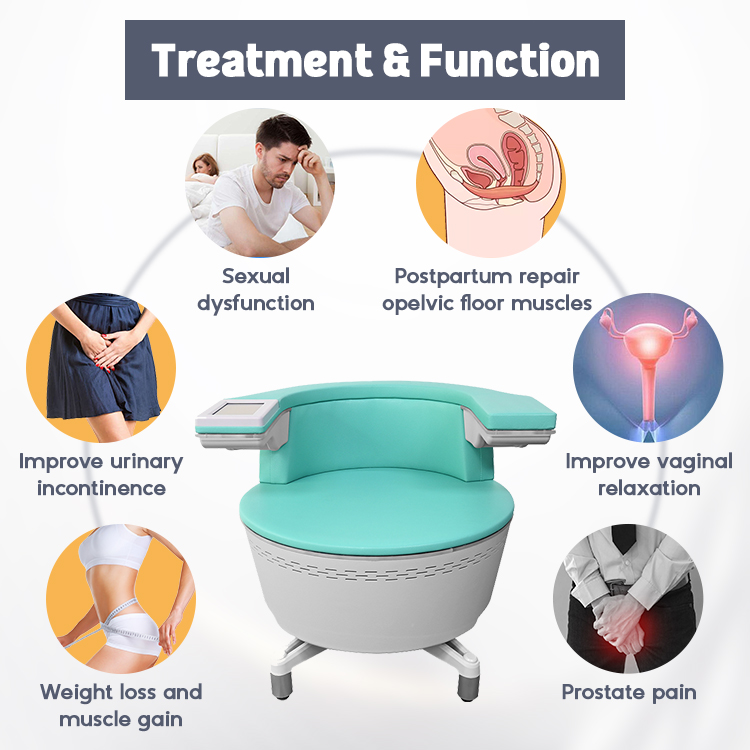
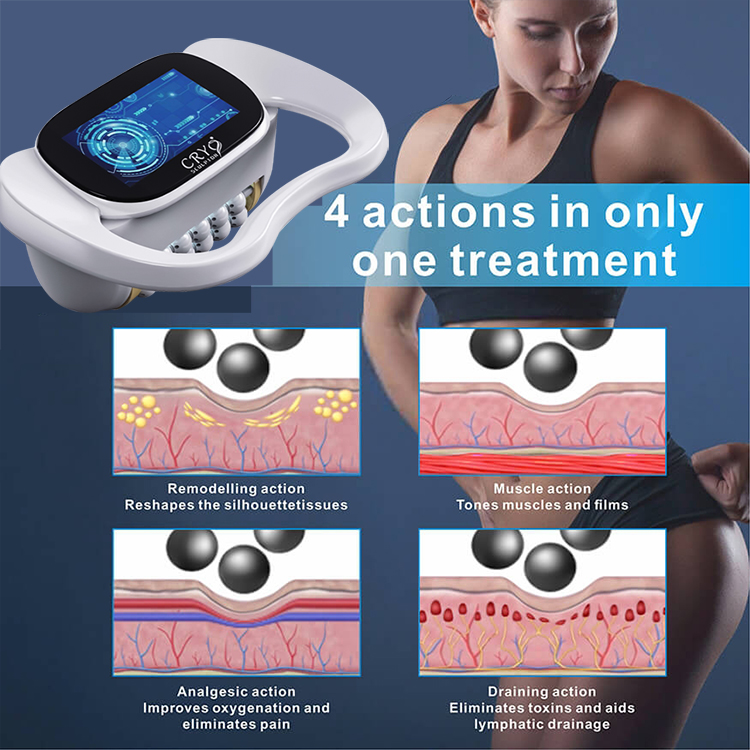
Physical rehabilitation has evolved significantly with the introduction of advanced therapeutic technologies. While traditional physical therapy remains a foundational approach for recovery and mobility improvement, physio magneto therapy has emerged as a modern, non-invasive alternative or complement. Understanding the differences between physio magneto therapy and traditional physical therapy helps clinics, practitioners, and patients choose appropriate rehabilitation strategies based on individual needs, treatment goals, and clinical settings.
1. Understanding the Two Treatment Approaches
1.1 What Is Physio Magneto Therapy?
Physio magneto therapy, often referred to as pulsed electromagnetic field therapy (PEMF) or PMST therapy, uses controlled electromagnetic fields to stimulate tissues at a cellular level. The therapy aims to support pain relief, improve circulation, and enhance the body’s natural recovery processes without direct physical manipulation.
Modern systems such as Shefmon’s combination magnetotherapy platforms integrate electromagnetic stimulation with adjustable parameters to suit different rehabilitation scenarios.
https://shefmon.com/product/a0275e-3-in-1-combination-machine-pmst-wave-magnetotherapy/
1.2 What Is Traditional Physical Therapy?
Traditional physical therapy relies on manual techniques, guided exercises, stretching, and physical manipulation performed by trained therapists. It focuses on restoring movement, strengthening muscles, improving joint mobility, and retraining functional patterns through repeated physical engagement.
This approach emphasizes therapist-patient interaction and active participation from the patient throughout the rehabilitation process.

A0275E Macchina combinata 3 in 1 Magnetoterapia a onde PMST
2. Core Mechanism Differences
2.1 Electromagnetic Stimulation vs Manual Intervention
Physio magneto therapy works by delivering electromagnetic pulses that penetrate tissues without physical contact. These pulses interact with cells, nerves, and muscles, potentially influencing pain perception and tissue recovery.
Traditional physical therapy, in contrast, depends on hands-on techniques and active exercises to mechanically stimulate muscles, joints, and connective tissues.
2.2 Depth and Targeting of Treatment
Electromagnetic fields can reach deeper tissue layers without increasing surface pressure, making physio magneto therapy suitable for patients who experience discomfort with manual manipulation. Traditional therapy may require significant pressure or repetitive movement to achieve similar depth, which can be challenging for some individuals.
3. Patient Experience and Comfort
3.1 Non-Invasive Nature of Physio Magneto Therapy
Physio magneto therapy is generally described as comfortable and passive. Patients remain relaxed during sessions while electromagnetic stimulation is applied. This makes it particularly suitable for individuals with acute pain, limited mobility, or low tolerance for manual pressure.
Devices such as the PMST NEO electromagnetic pain relief system are designed to deliver controlled stimulation with minimal discomfort.
https://shefmon.com/product/a0271e-pmst-neo-electromagnetic-pain-relief-treatment/
3.2 Active Participation in Traditional Physical Therapy
Traditional physical therapy requires active engagement, including exercises and movement training. While this participation is essential for functional recovery, it may cause temporary discomfort, especially during early rehabilitation stages.
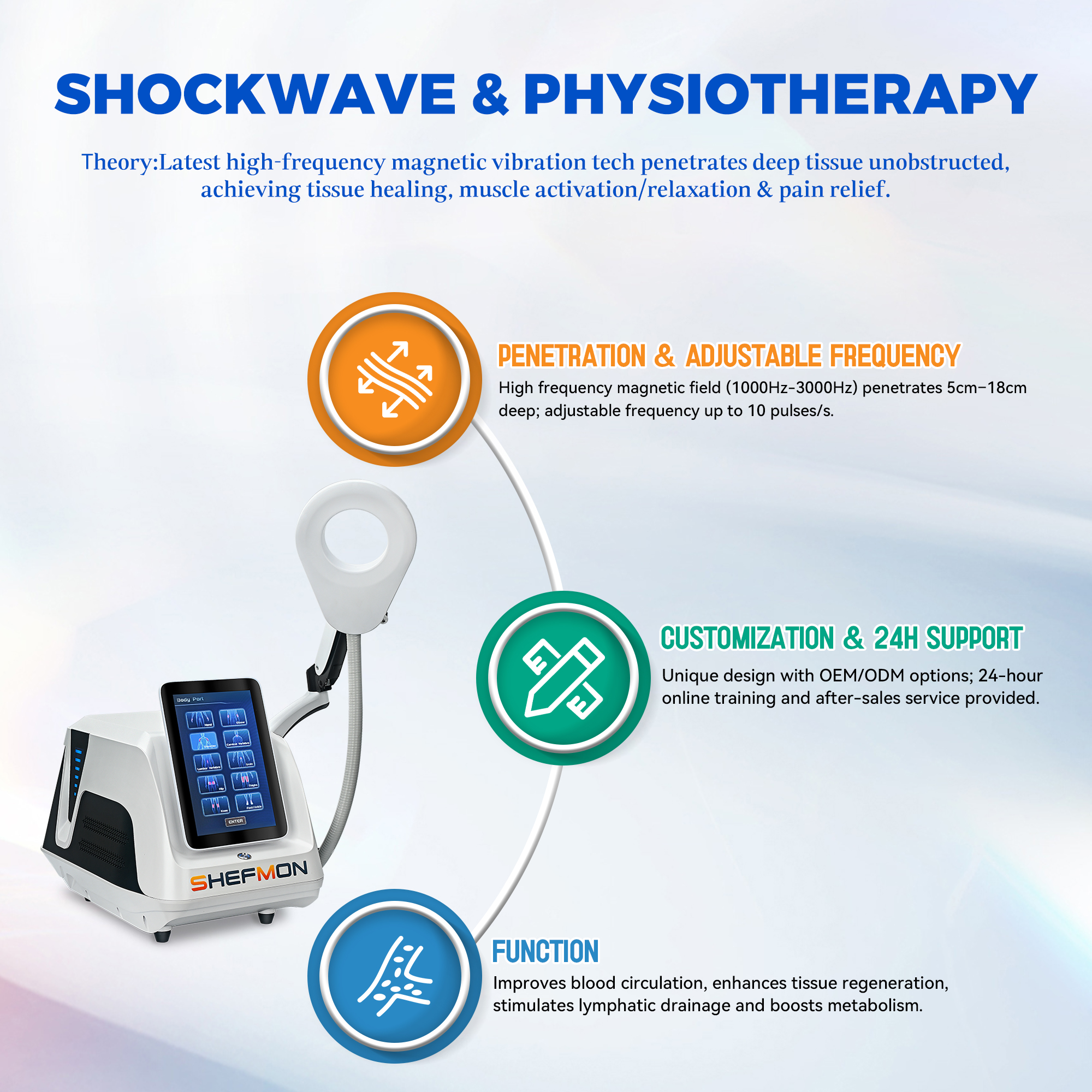
4. Treatment Scope and Clinical Applications
4.1 Conditions Commonly Addressed by Physio Magneto Therapy
Physio magneto therapy is often used as part of pain management and rehabilitation programs for musculoskeletal discomfort, joint stiffness, post-injury recovery, and chronic conditions. It is commonly applied as a supportive modality rather than a standalone solution.
4.2 Conditions Best Managed by Traditional Physical Therapy
Traditional physical therapy excels in restoring movement patterns, improving muscle strength, and retraining coordination. It is essential for rehabilitation following surgery, neurological injury, or musculoskeletal dysfunction that requires active re-education.
5. Treatment Efficiency and Time Considerations
5.1 Session Structure in Magneto Therapy
Physio magneto therapy sessions are typically standardized, with predefined durations and intensity settings. This consistency allows clinics to manage patient flow efficiently while offering predictable treatment experiences.
5.2 Therapist Dependency in Traditional Physical Therapy
Traditional physical therapy is highly dependent on therapist expertise and availability. Each session requires direct supervision, which can limit scalability and increase labor demands in busy clinical environments.
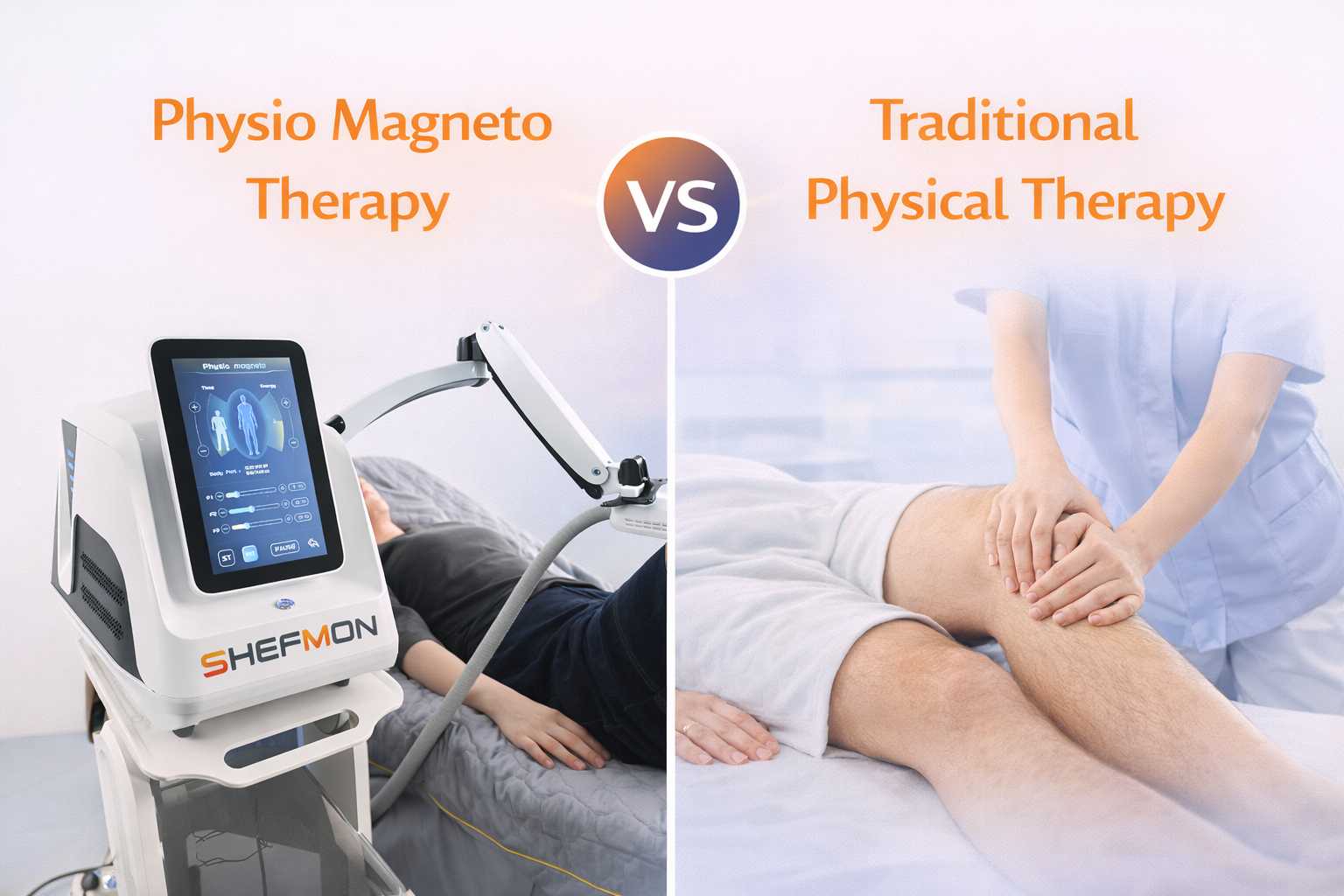
6. Customization and Treatment Planning
6.1 Parameter Adjustment in Magneto Therapy Systems
Advanced physio magneto therapy machines allow practitioners to adjust frequency, intensity, and treatment duration. This flexibility supports personalized care while maintaining standardized protocols across patients.
6.2 Individualized Exercise Programs in Physical Therapy
Traditional physical therapy offers highly individualized exercise programs tailored to patient progress. While this personalization is beneficial, it requires continuous assessment and therapist involvement.
7. Integration and Complementary Use
7.1 Combining Both Approaches
Rather than viewing physio magneto therapy and traditional physical therapy as competing methods, many clinics integrate both. Magneto therapy can be used to reduce pain and improve comfort, enabling patients to participate more effectively in active physical therapy sessions.
7.2 Optimizing Rehabilitation Outcomes
A combined approach often leads to improved patient compliance, smoother recovery progression, and more comprehensive rehabilitation outcomes.
Conclusione
Physio magneto therapy and traditional physical therapy represent two distinct yet complementary approaches to rehabilitation. Physio magneto therapy offers non-invasive, comfortable electromagnetic stimulation that supports pain relief and recovery, while traditional physical therapy provides active, hands-on techniques essential for restoring movement and function. Understanding their differences allows clinicians and patients to select or combine treatments based on specific needs, recovery stages, and therapeutic goals. When integrated thoughtfully, both approaches can play a valuable role in modern rehabilitation programs.