Partagez des solutions optimisées, des connaissances professionnelles en matière de vannes et des actualités du secteur
Veuillez saisir les termes ou mots-clés pertinents que vous souhaitez consulter ; les articles pertinents apparaîtront dans les résultats de recherche. Si vous ne trouvez pas la réponse à votre question, n'hésitez pas à nous contacter ; nous serons ravis de vous aider. Vous pouvez également nous envoyer un e-mail directement à beauty@shefmon.com.
L’incontinence urinaire peut-elle être guérie ?
machine emsculpt pour l'emsculpture corporelle
Introduction
Have you ever found yourself leaking urine when laughing, sneezing, or running? You’re not alone. Millions of people experience urinary incontinence—a condition that affects both men and women, though it’s especially common among women after childbirth or menopause. But here’s the big question: Can urinary incontinence be cured?
Let’s uncover the truth about causes, treatments, and new technologies that offer hope for a long-term solution.
Understanding Urinary Incontinence
Qu’est-ce que l’incontinence urinaire?
Urinary incontinence (UI) is the involuntary leakage of urine, meaning you can’t always control your bladder. It can range from mild leaks to a complete loss of bladder control.
Common Types of Urinary Incontinence
Stress Incontinence – Leakage during coughing, laughing, or physical activity.
Urge Incontinence – A sudden, intense urge to urinate followed by leakage.
Mixed Incontinence – A combination of stress and urge types.
Overflow Incontinence – Bladder doesn’t empty fully, causing dribbling.
Functional Incontinence – Physical or mental barriers prevent reaching the toilet in time.
Causes of Urinary Incontinence
Physical Factors
Faiblesse des muscles du plancher pelvien
Grossesse et accouchement
Prostate issues in men
Nerve damage from diabetes or surgery
Hormonal and Lifestyle Influences
Menopause leading to estrogen decline
Obesity increasing bladder pressure
Excess caffeine or alcohol intake
Certain medications (like diuretics)
Who Is at Risk?
Women and Childbirth
Women are more prone to incontinence due to pregnancy, vaginal delivery, and hormonal changes.
Aging Population
As we age, the bladder and pelvic muscles naturally weaken, increasing the risk.
Medical Conditions
Diseases like Parkinson’s, diabetes, or stroke can disrupt nerve signals controlling the bladder.
Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore
Frequent, sudden urges to urinate
Leakage during laughing, coughing, or exercise
Nighttime urination (nocturia)
Constant dribbling
Feeling of incomplete bladder emptying
If these symptoms interfere with daily life, it’s time to seek medical advice.
L’incontinence urinaire peut-elle être guérie ?
Here’s the good news: many cases can be treated—and even cured.
The outcome depends on the type, cause, and severity. Some people recover completely, while others manage their symptoms effectively through lifestyle changes or medical intervention.
Lifestyle Changes for Incontinence Control
Simple habits can make a big difference:
Diet and Hydration
Avoid caffeine, spicy foods, and alcohol.
Drink enough water, but not excessively.
Prevent constipation by eating fiber-rich foods.
Exercise and Weight Management
Extra weight puts pressure on your bladder. Losing even a few kilos can improve control significantly.
Pelvic Floor Exercises (Kegels)
How They Work
Kegels strengthen the muscles that support the bladder and urethra, preventing leakage.
Step-by-Step Guide
Identifier les bons muscles (arrêter la miction en cours de route).
Squeeze and hold for 5 seconds, then relax for 5.
Repeat 10–15 times per session, three times a day.
Stay consistent for visible results in a few weeks.
Medical Treatments and Devices
Medications
Doctors may prescribe drugs that calm overactive bladders or improve muscle tone.
Surgery Options
For severe cases, procedures like bladder sling surgery ou artificial sphincter implants can restore control.
Innovative Therapies
Minimally invasive treatments—like injections and nerve stimulation—are offering new hope for lasting improvement.
Traitements non chirurgicaux
Electrical Stimulation
Targets pelvic floor nerves to enhance muscle contraction and coordination.
Biofeedback
Teaches you how to control pelvic muscles effectively with visual guidance.
Bladder Training
Involves scheduled urination to gradually increase bladder capacity.
The Role of Technology in Treatment
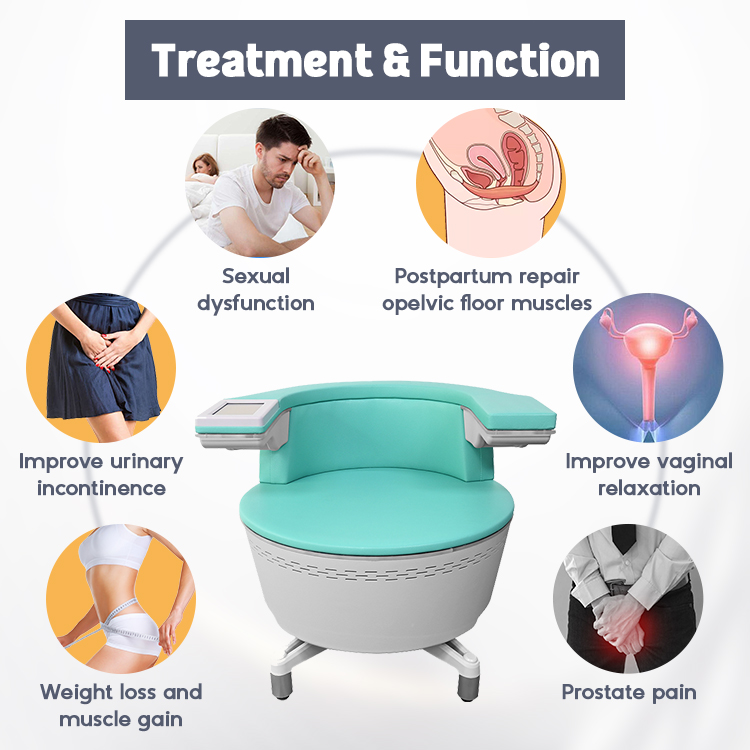
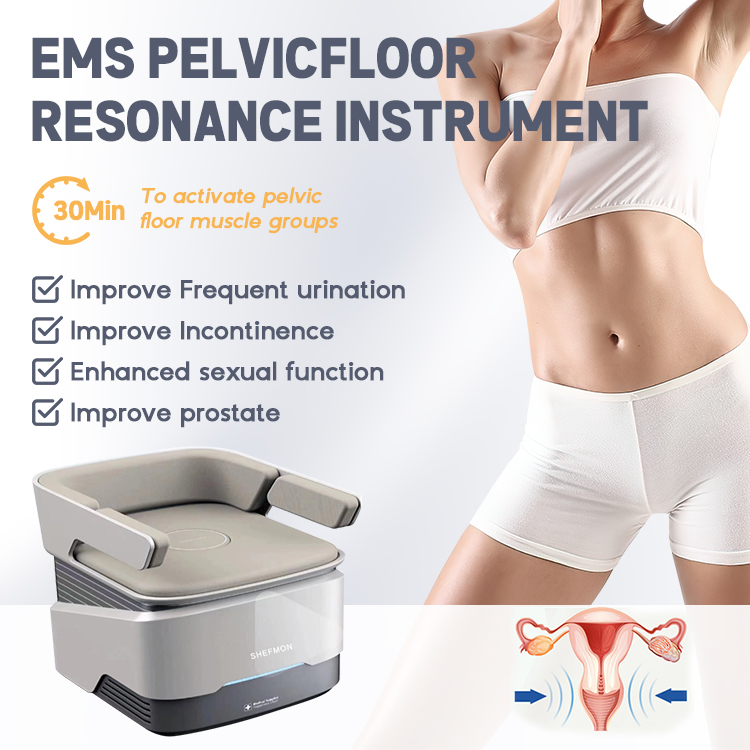
EMS (Electromagnetic Muscle Stimulation) Chairs
EMS therapy uses high-intensity electromagnetic waves to stimulate and strengthen pelvic floor muscles—without any invasive procedure or discomfort.
Des appareils comme le SHEFMON EMS Pelvic Floor Chair et SHEFMON Electromagnetic Stimulation Chair deliver thousands of Kegel-like contractions per session, helping patients recover bladder control faster.
These innovative machines are especially beneficial for:
Récupération post-partum
Menopause-related incontinence
Pelvic floor rehabilitation
They offer non-surgical, painless, and effective results, making them popular among clinics and wellness centers.
Preventing Urinary Incontinence
Maintenir un poids santé
Do regular Kegels
Avoid smoking (reduces coughing that strains muscles)
Treat chronic constipation
Stay active and hydrated
Emotional and Psychological Support
Dealing with incontinence can be emotionally draining. Support groups, counseling, or talking to your doctor can help reduce anxiety and embarrassment.
When to See a Doctor
If incontinence is affecting your daily routine, seek help early. The sooner it’s diagnosed, the more effective the treatment will be.
Conclusion
Donc, can urinary incontinence be cured?
In many cases—yes. With consistent exercises, lifestyle adjustments, and modern technologies like EMS therapy, most people regain control and confidence. You don’t have to live with the embarrassment or inconvenience. Seek help, explore your options, and take the first step toward a leak-free life.
FAQ
1. What is the best treatment for urinary incontinence?
The best treatment depends on the cause, but a combination of Kegel exercises, EMS therapy, and lifestyle changes works effectively for most people.
2. How long does it take to see results from pelvic floor therapy?
You may notice improvements after 4–6 weeks of consistent practice.
3. Can men also benefit from EMS pelvic chairs?
Yes! These chairs are effective for both men and women suffering from weakened pelvic muscles or post-surgery incontinence.
4. Is urinary incontinence permanent?
Not necessarily. Many cases are temporary and improve with proper treatment.
5. Can home remedies cure urinary incontinence?
While home remedies help manage symptoms, combining them with professional treatments like EMS therapy ensures faster recovery.